
In this article, we will analyze together how search engines work and what activities we need to perform in order to place our site content on the top search results.
We assume that Google does not have infinite resources(crawl budget), which is why it is essential to optimize our website so that google can detect, crawl and index as many pages as possible.
If you are an Entrepreneur, or a Marketing or Sales Director you know perfectly well that it is extremely important to be first on the SERP of Google (list of results when we perform a search).
Being first on search engines means greatly increasing the sales opportunities of your products and services and the visibility and notoriety of your Brand.
Crawling depth is a technicality that is part of a company’s SEO Strategy.
To achieve this important goal, our SEO Strategy must consider multiple factors:
- Quality of content
- SEO Positioning of Competitors
- Keywords used by users to perform searches
- Organization of new content on our site (Navigation Tree)
- Presence of keywords in articles published on our site
- Inserting internal links to the site to improve its navigability (Internal link building strategy)
- Placement of content about us, on third-party sites, that contains a link back to our site(External link building strategy)
Crawler: what it is and how Web crawling works
Definition: Crawler: automatic software or script that systematically inspects the keywords, content type, and links of a Web site, returning the information to search engines.
A crawler-also known as a bot, automatic indexer, or spider-is used by search engines to gather all the information needed to automatically index pages from the Web.
In addition, crawlers also help validate HTML codes and verify hyperlinks on each page.
The first step a spider performs when it comes across your website is to look for a file called “robots.txt.”
This file is critically important, because it contains all the instructions for the bot: which parts of the website to index and which to ignore.
Google crawler: practical example
Take the Google search engine as an example: the bot analyzes each of the indexed pages in its database and retrieves those pages on Google’s servers.
The web crawler follows all hyperlinks in websites and also visits other websites.
When we ask the search engine, for example, for a “search engine optimization strategy,” we will have as a result all the web pages that contain the keyword typed.
Automatic indexers are programmed to constantly scan the Web so that the results generated are always up-to-date.
Web crawling: how it works
When we talk about web crawling (from English = web crawling), we mean that process put in place by all search engines, to gather information from the pages of each website.
The crawlers need to know, first of all, that your website exists so that they can come by to take a look. Therefore, an entry point is needed to perform the crawl.
If you have recently created the site, we recommend that you apply to Google for relevant indexing.
If you have built your site in WordPress, we recommend that you install the Yoast SEO Premium Plugin and, via Google Search Console, notify Google of your sitemaps.
Once a crawler lands on your website, it begins mapping all its elements-from content to inbound and outbound links, and so on.
Let’s say that, eventually, everything on the Web will be found and “spidered.”
Basically, there are 3 steps that a bot takes:
- Initial search and scan of the website
- Keyword and site content indexing
- Mapping hyperlinks (Web page addresses or URLs) found within the site
How to manage the depth of the Google crawler
When we talk about SEO crawling, we mean that process put in place by all search engines, to gather information from each website.
Let me explain further.
Google, to verify a site’s information, uses an army of spiders (spiders, or bots), which roam the Web with the goal of capturing the most relevant information, depending on specific keywords.
So, in order for Google’s 8-legged army to find us, we will have to feed these spiders–don’t you think?
This is where our SEO Strategy comes in, which helps us climb the Google rankings, thanks to the keywords and valuable content we are going to make.
But let’s go step by step.
By the end of this article you will be clear on how IT crawling works, and you can use all this information to improve the Strategy for your Company. Or. if you prefer, you can ask for an SEO consulting from our Agency.
Google crawler: scanning the search engine
Web crawling (from English “web scanning”), is the process put in place by Google’s spiders to visit a page, download it and check for external links.
In this way, our spider army has the opportunity to capture additional information, including from related pages through link building.
The more our page is able to attract spiders, the more often it will be scanned by web crawlers, looking for content updates and changes.
Therefore, if we feed Google’s spiders consistently, and with quality content, they will be incentivized to come back to us.
Conversely, if we try to feed them with “junk food,” or trite content, they will soon get bored and look for more quality elsewhere.
Talking about spiders, and the methods by which to feed them, scares me too. I hope I made the point, though.
How does web scanning work?
As we mentioned, search engines use spiders (or bots) to discover the most interesting web pages, and analyze them end-to-end.
Or rather, from the header (head of a site’s page) to the footer (foot of a site’s page).
And these spiders are called web crawlers.
First, all crawlers start crawling by downloading the robots.txt file.
This file is most important, as it carries sitemap information, URLs, and acts as a guide for search engines, advising which pages of the Web site to scan, or not.
Crawling processes, like most web processes, work through a special algorithm.
This is used to determine how often web crawlers should scan a page, and how many (and which) pages on the site deserve to be indexed.
For example, a page that is constantly updated or changed is more likely to be scanned multiple times than a section that reports updates infrequently.
Google crawler: scanning for (non-text) media files
Generally, all search engines attempt to scan, and index, all URLs they find along their path.
However, if a particular URL links to a non-text file, such as an image, video, or audio file, engine crawlers will only be able to read some data associated with this type of file. Such as the name, or their associated metadata.
But let’s not give up.
Although search engines can only read some information from non-text files, we still have the ability to index them, to make sure that we generate traffic to our site.
Scan and extract links
Crawler spiders, discover new pages online by scanning a website they already know, and its pages.
Once the internal links of the scanned pages are identified, they proceed to extract the links. To find new URLs, from which to retrieve more information.
Thus, using an internal link building strategy, in addition to providing a better experience for users, visitors to our site, allows internet crawlers to find more and more information, making our page more interesting in their “eyes.”
In this way, we incentivize the action of spiders to rescan the pages of our site, making them increasingly attractive, and indexed, by search engines.
Sitemap
Crawling sitemaps is another technique used by search engines to find new pages on the Web from which to retrieve information.
Sitemaps are files with an .xml extension that contain a list of your site’s content to be indexed.
They are a great tool for providing search engines with a real list of pages to scan and index.
Within sitemaps, it is also possible to include other pages of our site, where, for example, internet crawlers can find more “hidden” content.
If your website is developed in WordPress, we recommend using the Yoast Seo plugin, which offers lots of important features for writing content in compliance with the rules and your SEO Strategy.
One of these features is precisely about creating and updating site sitemaps.
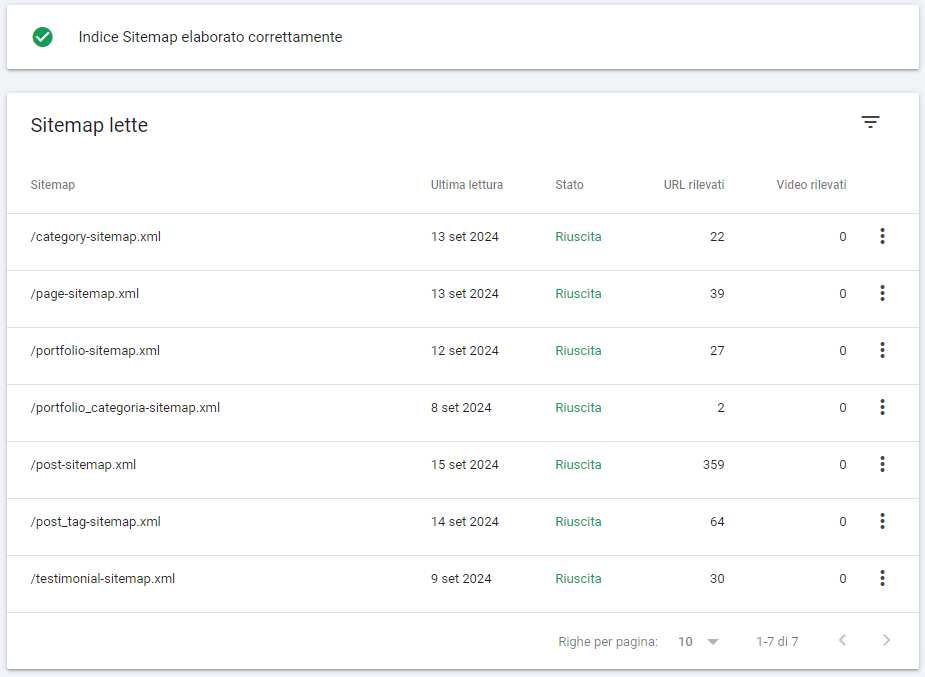
The image shows the list of xml sitemaps of our site generated directly from the Yoast SEO Plugin. As you can see they are divided by content type, so Google knows, right away, if a sitemap contains articles, or products, tags, categories etc.
Once the sitemaps have been generated with Yoast Seo, it is essential to notify Google Search Console, the free Google service that allows us to check and optimize our website’s SEO strategy in the best possible way.
If you don’t know how to do it read our SEO Glossary Post: Procedure for submitting Sitemap to Google Search Console
Tools to be used for proper site indexing
There are some online tools that can be of great help in indexing our web pages. We at Factory Keywords recommend some of them:
- Google Search Console
- SemRush
- Google Analytics
- Google Keyword Planner
With this article we hope to have cleared up some doubts regarding the Google Crawler.
However, if you have any concerns, please write your questions to us in the comments.
We will be happy to address any of your concerns.
