Google Search Console if you want to do SEO you need to know it!
If you have a Web site or an e-commerce you know perfectly well that, having SEO ranking on search engines, is crucial for the growth of your Business.
Being first on Google and other search engines means intercepting new potential customers and strengthening your company’s image.
As is the case with any Marketing Strategy, one of the key elements for winning in the market and defeating the competition is data.
Data are critical to understanding:
- Where our Business Comes From
- Which channels convert the most?
- Which ads have the highest conversion?
- How is our target audience segmented?
- Which keywords attract the most users and have the highest conversion rate?
These are just some of the questions we need to answer every day to prepare an effective marketing and business strategy.
In this article you will find a key Google service for analyzing data and growing your Business.
Google Search Console. What it is.
If you are wondering what Google Search Console is for, we can tell you that it is a very powerful service offered by Google that allows us to check our site, in terms of indexing and search engine optimization.
Basically, Google Search Console is essential for monitoring and updating our Search Engine Optimization Strategy.
This tool helps us check what works, and what doesn’t, on our website.
With Google Search Console we can:
- Check the Sitemap
- Completely scan our site, looking for malware, blocked pages, etc.
- Check for errors on the pages of the site
- Find out which keywords brought users to our site
- Check for problems on security
In addition to being free, it offers useful tips to improve our SEO ranking strategy.
Google Search Console: what can I monitor?
If we want our website to be properly ranked on Google SERP, it is essential to perform some activities:
- Notify Google of the sitemaps on our site
- Through the Console you can progressively monitor which content is indexed and which is not
- You can detect and fix the problems that block each individual page.
It is useless to invest time and money in the strategy of SEO Copywriting if our content is not seen correctly by Google.
We report some of the most important functions and graphs of Google Search Console.
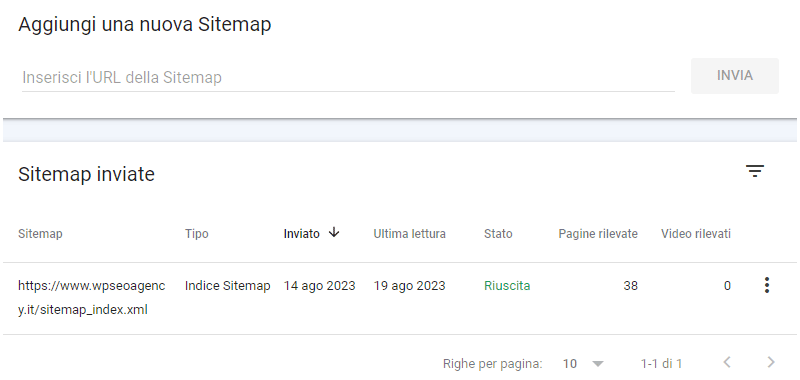
Google Search Console Sitemap management
In this section of the console you can submit your site’s sitemaps to Google.
A sitemap is a file, usually in XML format, that hierarchically lists all the URLs of a Web site and related information (e.g., date last updated, frequency of changes, language versions).
It is used by search engines to efficiently scan, understand and index the pages and content of the site.
If your site was developed in WordPress we recommend you read this article: WordPress Sitemap: How to notify Google about them?
Google Search Console crawl reports
In GSC you can monitor in detail every activity concerning the performance of your website or eCommerce.
Below you will find the explanation of the main features and let’s see together how Google Search Console works.
Yield in search results
In this section of the console you can view the “Yield in search results” broken down by:
- Total clicks: Number of clicks to your website
- Total impressions: how many times your site’s Snippets appeared on Google’s SERP
- Average CTR: Acronym for Click-Through Rate expresses the percentage of impressions that generated a click. When this value is high, it means that your content intercepts a lot of users on the search engine.
- Average position: Expresses the average position of your content on Google’s SERP.
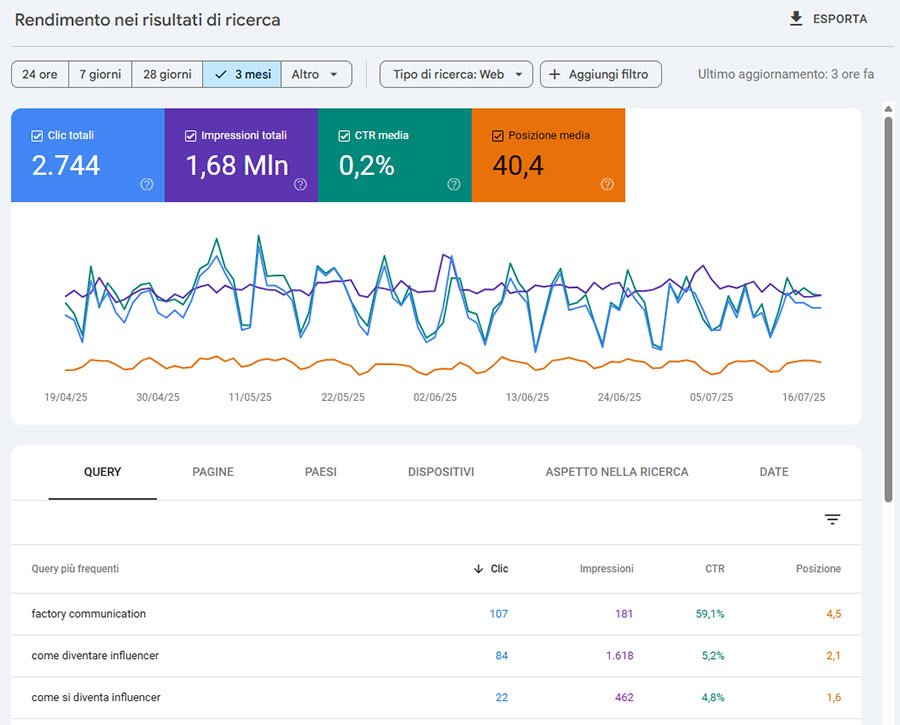
As you can see in the image you can define the time frame: 24 hours, 7 days, 28 days, 3 months, or you can customize it to your liking.
You can also add different filters to further verticalize the analysis.
The section below the graphs shows data on:
- Search queries: what keywords users used to get to your sit
- Pages: Traffic for each individual page
- Countries: traffic segmentation based on country of click origin. This data can be very useful if your Company also present in foreign markets and if your site is multi-language.
- Devices: this section is very useful because it allows you to understand whether your site is viewed more on desktop, or on mobile devices. This information is very useful for deciding on the formatting of page content.
- Dates: a summary of data broken down by date
I recommend that you export and analyze this report at least 1 time every 3 months.
N.B. By “Pages” Google means “Permalink” i.e., it considers even a single image to be pages.
Page indexing
This chart is extremely useful because it allows you to quickly see how many pages have been indexed and how many have not.
You can do a thorough check using the selector we have highlighted with the yellow box.
Thanks to the selector for example you can check:
- all the pages you “submitted” to Google
- the pages that you did not submit but were detected
- the pages in the sitemaps
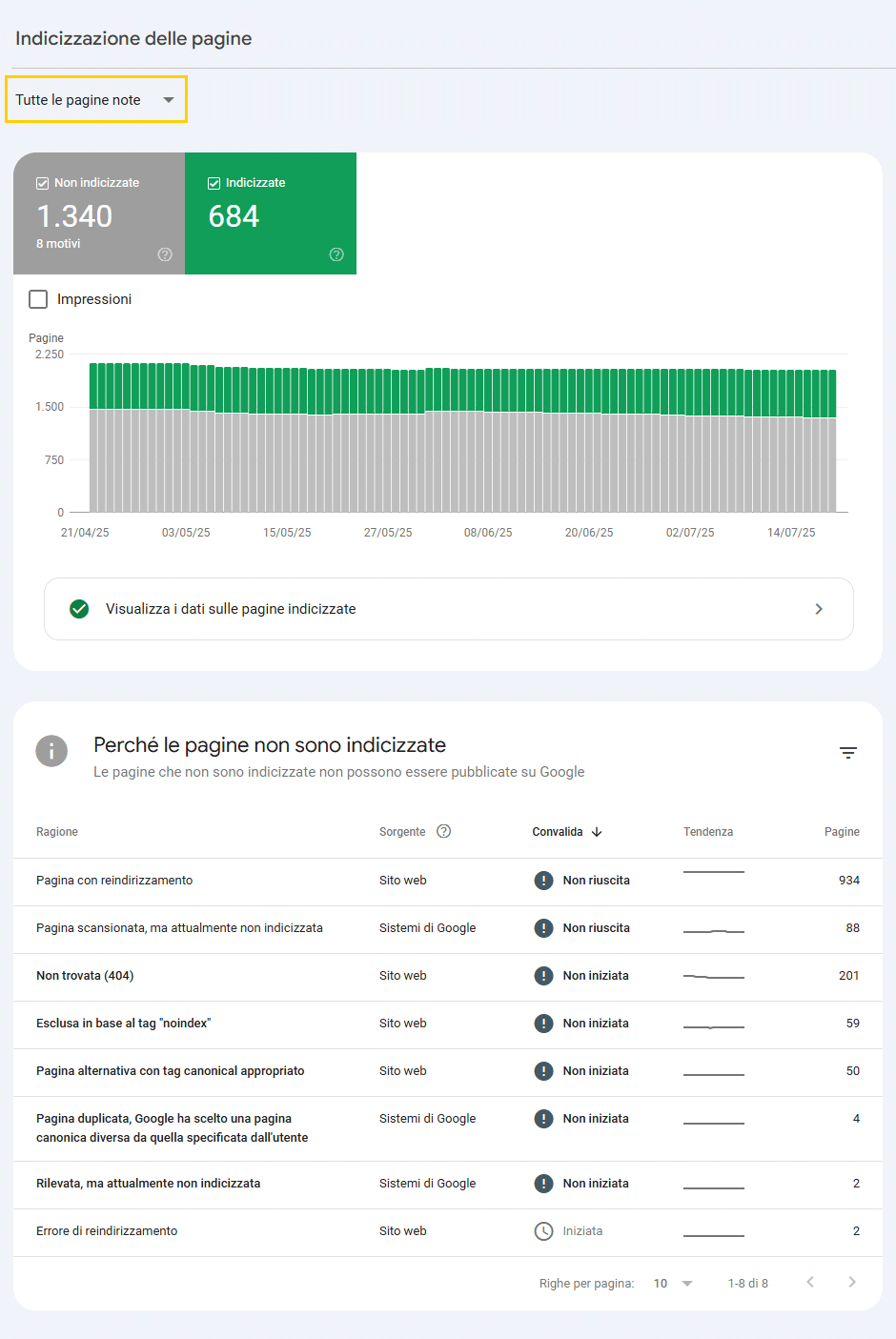
This report is extremely important because it allows you to understand and verify:
1. Page with redirection
How many and what they are. beware that you will also find some pages that I would call strange, that is, they are portions of permalinks that don’t make sense. They are probably the result of some scanning error.
2. Page scanned, but not currently indexed
This report can be very useful for you to understand the indexing status of your content.
Consider that if you have communicated your website’s sitemap, every time I publish content it is automatically detected by Google’s Bots.
In this section of the report you can figure out which pages you have not yet indexed.
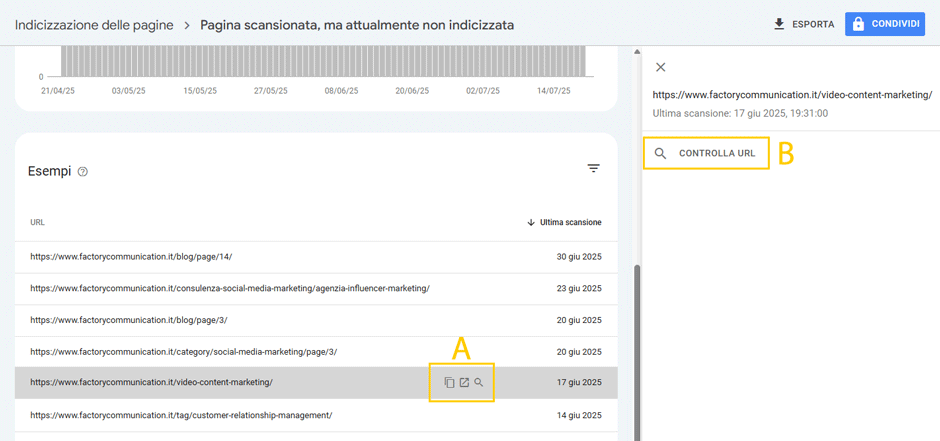
By clicking on the link you can immediately (letter A) you can check if the page exists.
By clicking “Check URL” (letter B) you can ask Google to check the indexing status of the page.
A new page will appear telling you that“The URL cannot be found on Google.”
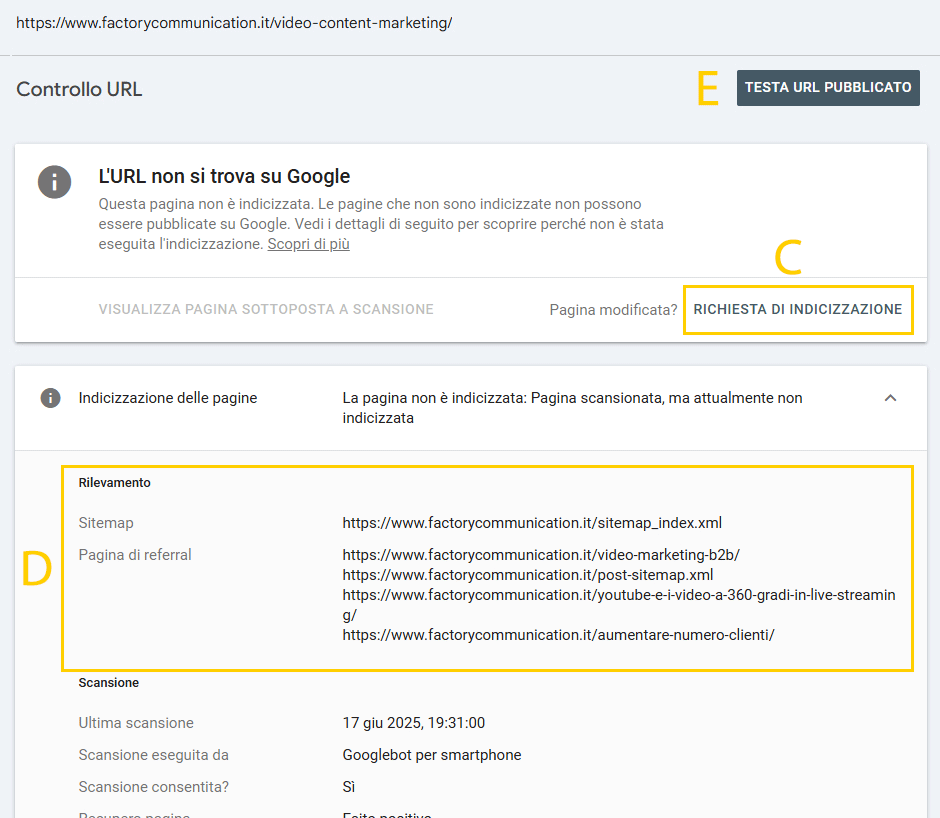
At this stage you can send Google a“REQUEST FOR INDICATION” (letter C), however first I recommend that you check the data in the Report such as “Sitemap” and “Referral Page” (letter D).
If Google has identified a different Referral page you need to understand why it considers another page more appropriate for your content.
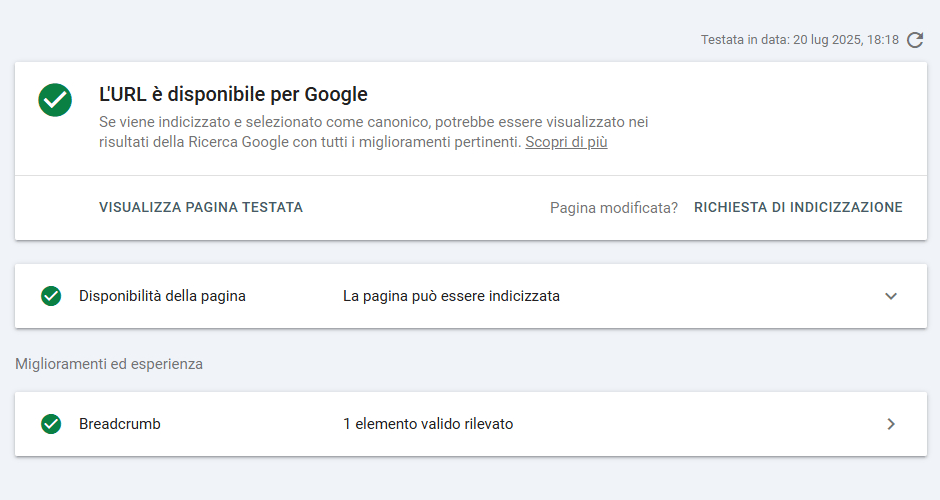
Regardless, before submitting the INDEXING REQUEST, I recommend that you perform a “PUBLISHED URL TEST” that way you will be sure that the page conforms to Google’s standards.
The following notice will appear for you:
3. Not found (404)
I recommend that you analyze this report carefully because it could be very useful for you to check the content of your website. Maybe you have deleted pages in the past without applying a redirect.
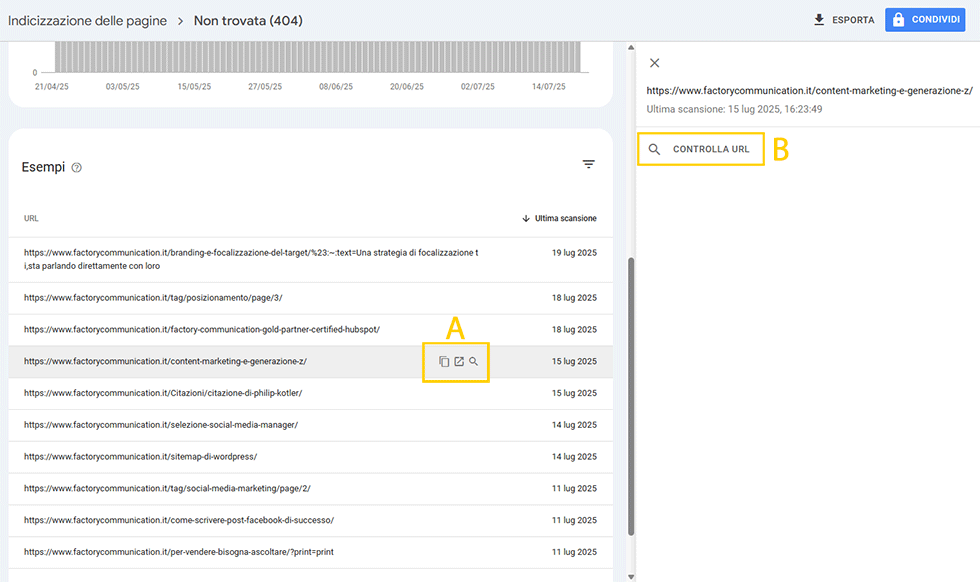
By clicking on the link you can immediately (letter A) you can check if the page does not exist.
If the page does not really exist I suggest you check to see if Google has indexed it by clicking “Check URL” (letter B).
If the page is not listed on Google you can ignore this Alert.
If, on the other hand, the page should show up on Google then I recommend that you do a redirect to an existing page on your site with similar content.
4. Excluded based on the “noindex” tag.
“Noindex” is a specific tag you can use to ask Google not to index a piece of content. For example, Login pages or some eCommerce pages are set “noindex” for security issues.
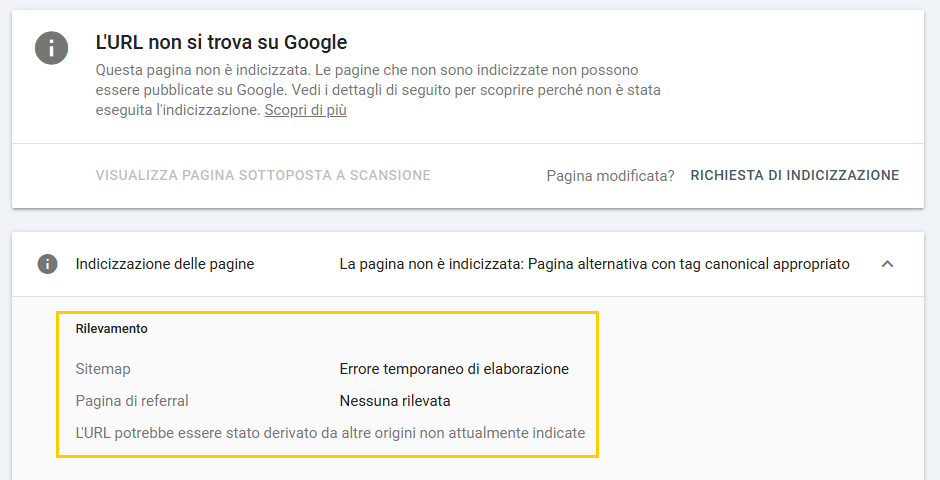
5. Alternative page with appropriate canonical tag
This report allows you to see if Google has chosen specific pages.
From our experience, if you ask a you will find that most of these links do not exist in fact it is Google itself that says “The URL may have been derived from other origins not currently indicated.”
6. Duplicate page, Google chose a different canonical page than the one specified by the user
This case also closely resembles previous situations.
In our case, for example, Google had indexed some pages of our Blog.
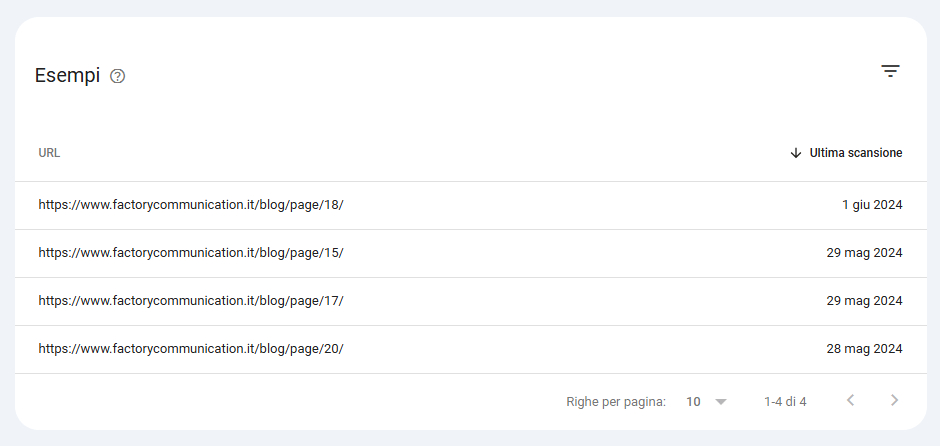
Next, we removed the layout function of WordPress and inserted the function that allows you to progressively download content.
At that point the layout was removed but Google still retained some links that it progressively no longer considers.
7. Detected, but not currently indexed
This report is very important. Consider that the more content you publish, the greater the “visit” of Google spiders predisposed to detect new content.
If you have published important content and it has not yet been indexed, I recommend that you submit an indexing request yourself.
8. Redirection error
The last report allows you to check the redirects of pages on your site.
Whenever you feel you have resolved one or more issues, you can request verification from Google by clicking “VALIDATE CORRECTIONS.”